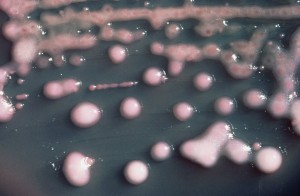
The study provides new evidence that the livestock-associated CC398 strain could spread in hospitals, including those with newborn babies. From farm animals is resistant to some common antibiotic drugs, which could make it harder to treat.
The strain’s enhanced drug resistance in livestock is likely the result of widespread use of antibiotics on farms, scientists say. Patients in hospitals and nursing homes are at increased risk of MRSA infection, but healthy people in the wider community can also become infected.
Some MRSA bugs in UK hospitals can be traced back to a type of bacteria found in farm animals, a study suggests.
A strain of drug-resistant bacteria carried by some livestock – the MRSA strain Staphylococcus aureus CC398 – has also been found in patients, researchers say.
People and animals generally harbour distinct variants of CC398, which the team say evolved from the same original bacteria. However, the CC398 strain found in livestock can be transmitted to humans, and the study shows that this has happened on many occasions.
The study, published in the journal Applied and Environmental Microbiology, provides new evidence that the livestock-associated CC398 strain could spread in hospitals, including those with newborn babies.
Scientists at the University of Edinburgh studied how the CC398 strain evolved using a state-of-the-art genetic analysis technique. For the first time, researchers unravelled the full genetic code of CC398 strains from the UK, and compared these with …
An alternative approach to the antibiotic resistance problem is to interfere with the mechanisms that promote resistance, rather than to attempt to kill the bacteria. For example, interfering with the duplication or movement of a bacterium's genetic material would eliminate the transfer of resistance genes between bacteria.
Please Read this Article at NyrNaturalNews.com




Leave a Reply